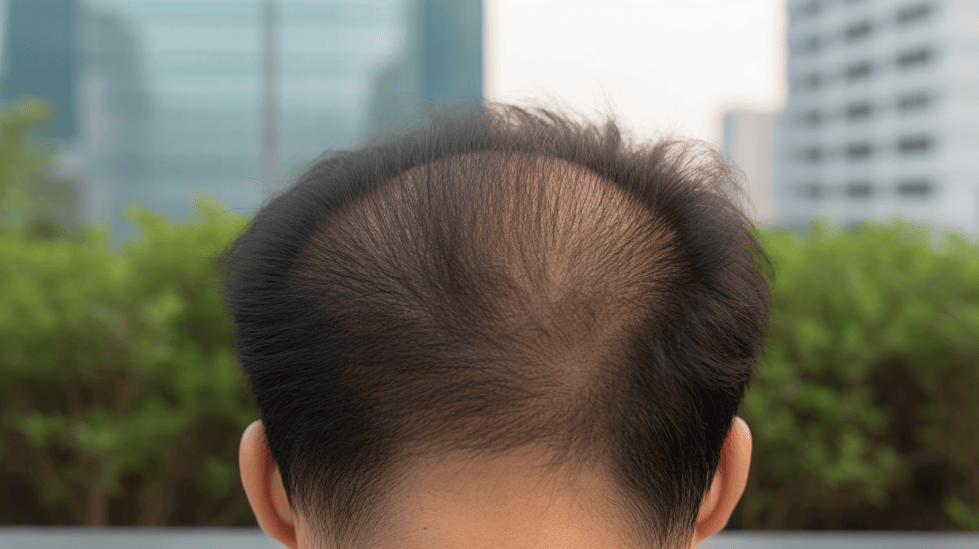
When Does Men’s Hair Start Thinning
As someone who has experienced hair thinning, I know all too well the anxiety and frustration that comes with the early onset of hair loss in men. Hair thinning in men is a common issue that can begin as early as the late teenage years, with some men experiencing hair loss before the age of 21. In fact, according to a source, almost 25% of men start losing their hair before they even hit their twenties.
By the time most men reach the age of 35, the number of those experiencing hair loss increases to nearly 66%, and this percentage further goes up to 85% as they turn 50. The main cause for hair loss in men can be attributed to genetics, which also makes it difficult to predict exactly when a person should expect hair thinning. For many, receding hairlines begin to set in as an early sign of hair loss, typically occurring around the forehead and the top of the head.
It’s crucial to understand that while there is no concrete one-size-fits-all timetable for when hair loss begins in men, knowing the average age, the potential genetic predisposition, and learning about the early signs of hair thinning can help one take better care and treatment measures in advance. This approach may help slow down or manage the process of hair loss more effectively.
Understanding Hair Thinning and Hair Loss
As a person who has experienced hair thinning, I believe it’s essential to understand the difference between hair thinning and hair loss. In this article, I will discuss hair follicles, the hair growth cycle, and the causes of hair loss.
Hair Follicles
Our hair grows from hair follicles, which are tiny sacs in the skin where hair shafts form. The average scalp has around 100,000 hair follicles, and each one has its own life cycle. Hair thinning and hair loss occur when the life cycle of hair follicles is disrupted or when they are damaged.
Hair Growth Cycle
The hair growth cycle consists of three phases: the anagen (growth) phase, the catagen (transition) phase, and the telogen (resting) phase. Each hair follicle goes through these phases independently of the others, which is why we don’t lose all our hair at once. However, various factors can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to hair thinning or hair loss.
Causes of Hair Loss
There are several causes of hair loss, including medical conditions, medications, and genetic factors. The most common cause of hair loss in men is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness. This condition, which is linked to the effects of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on hair follicles, can be inherited.
Alopecia areata is another type of hair loss that affects both men and women. It is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair to fall out in small, round patches.
Telogen effluvium is a temporary hair loss condition that occurs when a large number of hair follicles suddenly enter the telogen phase. This can be caused by various factors, such as severe stress, illness, or rapid weight loss.
Other medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or nutritional deficiencies, can also contribute to hair thinning and hair loss. It’s important to consult a doctor if you suspect that your hair loss might be due to an underlying medical condition.
In conclusion, understanding the hair growth cycle and the various causes of hair loss can help us better manage and potentially prevent hair thinning and hair loss in our lives.
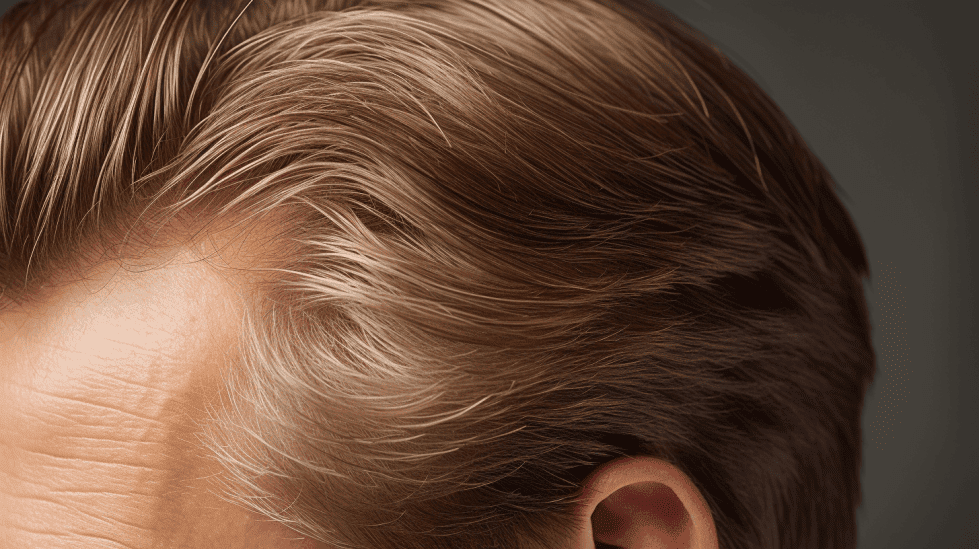
Signs and Symptoms of Thinning Hair
As I age, thinning hair is something I have come to encounter. There are various signs and symptoms that help me identify when my hair is thinning, and it is essential for me to understand these to address the issue early on. In this section, I will discuss the key indicators that my hair is thinning, including receding hairline, thinning crown, and the development of a bald spot.
Receding Hairline
When I noticed a receding hairline, it was one of the primary signs that my hair was beginning to thin. A receding hairline usually starts above the temples and gradually moves back across the top of the head (Healthline) . Over time, this can cause an “M” shaped hairline that is quite common among men experiencing hair loss.
Thinning Crown
Another sign of thinning hair that I became aware of was a thinning crown. This refers to the region at the top and back of my head, where hair tends to become finer and sparser (Healthline). Thinning in this area of the scalp can be more difficult to notice, as it isn’t as visible as other regions, but it is an essential sign of hair loss to pay attention to.
Bald Spot
Finally, the development of a bald spot on my scalp has been another indicator of hair thinning. A bald spot typically appears when the hair loss progresses, and it is more visible than a thinning crown or receding hairline. It can develop in different areas of the scalp, although it is most common at the crown of my head (Healthline).
Overall, identifying these signs and symptoms of thinning hair has helped me understand the progression of hair loss and should assist me in addressing it effectively.

Male Hair Loss Patterns and Causes
As someone who is well-researched in the field of hair loss, I find that a variety of factors contribute to the thinning of men’s hair. In this section, I’ll discuss the common causes and patterns of male hair loss, including genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors.
Genetic Factors
One of the primary causes of male pattern baldness is genetics. It’s a hereditary condition that results in a receding hairline and hair thinning on the top and front of the scalp. According to the DermNet NZ, it is also known as androgenetic alopecia. Family history plays a crucial role in determining the likelihood of developing this condition, and a specific gene on the androgen receptor, inherited from either parent, can be the culprit.
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal imbalances can also lead to hair loss in men, particularly the presence of male hormones called androgens. An enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase converts testosterone, the primary male hormone, into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is known to shrink hair follicles, causing the hair to thin and eventually fall out. There is also evidence linking hair loss with erectile dysfunction, and it’s believed that the hormonal changes that contribute to one may also impact the other.
Lifestyle and Health Factors
Aside from genetics and hormones, lifestyle factors can also influence hair loss in men. Some of these factors include:
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to a temporary form of hair loss called telogen effluvium, as mentioned by the Mayo Clinic. This causes hair to stop growing and eventually fall out, but it can be reversed by managing stress levels.
- Nutrition: A poor diet lacking essential nutrients can also contribute to hair loss, as hair follicles require proper nutrition for optimal health and growth.
- Medical conditions: Certain illnesses, such as thyroid disorders, anemia, or autoimmune diseases, can lead to hair loss. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy can cause temporary full-body hair loss.
- Smoking: Smoking can constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the scalp and depriving hair follicles of the nutrients they need, leading to hair loss.
Understanding the causes and patterns of hair loss can help men identify the factors influencing their hair thinning and take appropriate steps to maintain or regain a healthier head of hair.

Common Types of Hair Loss
In this section, I will discuss some common types of hair loss, including Androgenetic Alopecia, Alopecia Areata, Telogen Effluvium, and Tinea Capitis.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic Alopecia is the most common type of hair loss, affecting more than 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States. Also known as male pattern hair loss or female pattern hair loss, this hereditary condition can be managed with medication or surgery. For males, hair loss usually begins at the temples or on the top of the head. In contrast, women typically experience widespread thinning of the hair.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease that causes hair loss in small, round patches. The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss on the scalp and elsewhere on the body. The severity of this condition varies, and hair may regrow in some cases. Treatment options include corticosteroid injections, topical medications, and oral medications.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen Effluvium is a form of hair loss that occurs two to three months after a major body stress, such as a prolonged illness, major surgery, or serious infection. This temporary condition can be triggered by hormonal changes, certain medications, and physical or emotional stress. It is characterized by the shedding of large amounts of hair, often resulting in diffuse thinning. According to Harvard Health, the hair growth cycle usually returns to normal once the underlying cause has been resolved.
Tinea Capitis
Tinea Capitis is a fungal infection that causes scalp infections and hair loss, primarily affecting children. This contagious infection can spread through contact with infected people, animals, or contaminated objects. Symptoms include itching, scaling, and redness of the scalp, as well as brittle or broken hair. Treatment typically involves oral antifungal medications and medicated shampoos.

Preventing and Treating Hair Loss
As someone concerned about thinning hair, I’ve been researching various ways to prevent and treat hair loss. I discovered that there are several approaches, including medical treatments, surgical treatments, and lifestyle changes. In this section, I’ll discuss each of these options in detail.
Medical Treatments
One of the most popular medical treatments for hair loss is the use of an over-the-counter medication called minoxidil, commonly known as Rogaine. Minoxidil works as a vasodilator, which means it widens blood vessels, potentially increasing blood flow to the hair follicles and promoting hair regrowth. I found that the usual concentration recommended for men is 5%.
Another treatment option is the prescription medication finasteride, which is known to inhibit the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Since DHT is a main cause of hair loss in many men, blocking its production can help slow down hair thinning and even promote new hair growth.
Surgical Treatments
If medical treatments do not work for me, I can opt for a hair transplant surgery. This procedure involves removing hair follicles from an area with healthy hair growth and transplanting them onto the thinning or balding areas. This method is effective, but it can be costly and may require multiple sessions for the best results. Another surgical option is scalp reduction, where the areas with hair loss are removed, and the remaining scalp is stretched to cover the area.
Lifestyle Changes
I learned that lifestyle changes could also potentially improve hair health and slow down hair thinning. For example, maintaining a balanced diet with essential nutrients like vitamin B, vitamin D, and iron can promote healthy hair growth. Furthermore, managing stress levels and avoiding hairstyles that pull or tug on the hair can also help reduce hair loss.
Some natural remedies and supplements, such as saw palmetto and low-level laser therapy, have been suggested to promote hair regrowth, although their effectiveness varies.
Ultimately, the best approach for me will depend on the cause and severity of my hair thinning. To make a well-informed decision, I should consult with a healthcare provider for medical advice and discuss my options for hair loss treatments.

When Does Hair Thinning Start for Men
As someone who has researched hair loss extensively, I can confidently say that men’s hair thinning can start at different ages depending on various factors. Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in men.
Age and Hair Loss Progression
While there is no exact age that men start experiencing hair loss, it often becomes apparent in their 30s. Most men will experience some level of hair loss by the time they’re 85, and genetics play a significant role in determining the onset and rate of hair loss. However, young men and even teenagers can experience hair loss in extreme cases, making it essential to be aware of the early signs.
Early Signs and Detection
Identifying hair thinning in its early stages can be crucial for successfully managing and treating the condition. Some common early signs include:
- A receding hairline
- Thinning hair on the top of the head
- Widening of the part
- More hair shedding than usual
- A noticeably more visible scalp
Different men may experience these signs at different ages, and the rate of hair loss can vary significantly from one individual to another. To properly assess and diagnose hair loss, taking the time to observe these early signs can be tremendously helpful.
Coping with Hair Loss
As I started to notice my hair thinning, I realized it’s essential to find ways to cope with hair loss. According to the American Hair Loss Association, two-thirds of American men will experience some degree of appreciable hair loss, with 85 percent of men “significantly thinning” by the age of 50.
Embracing Baldness
One of the ways I came to terms with my hair loss was by embracing baldness. I decided to shave my head, which allowed me to feel more confident and present a clean, neat look. A shaved head can help minimize the appearance of thinning hair or bald patches. I found maintaining a healthy lifestyle, incorporating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly, can also contribute to the overall health of my hair.
Hair Replacement Options
If embracing baldness was not an option for me, there are other hair replacement options available. One popular method is hair transplantation, a surgical procedure where a doctor takes individual hair follicles from denser areas of the scalp and relocates them to thinning or balding areas. This can provide a long-term solution for hair loss, and the results often look natural.
Another option is using medications like Minoxidil or Finasteride, both of which are available in tablet form. These can help slow down the hair loss process and, in some cases, promote regrowth of hair. However, it’s essential to consult a doctor before starting any medication and to be aware that the results may not be the same for everyone.
Psychological and Social Impacts
I learned that losing hair can impact not only one’s appearance but also have psychological and social effects, such as lower self-esteem and negative self-perception. According to WebMD, a full head of hair is often considered attractive and masculine in our culture. For me, it was essential to accept that hair loss is a natural part of life and focus on other aspects of my personal and professional life to build up my confidence.